Selector function of MHC I molecules is determined by protein plasticity
 Model of MHC I peptide selection by Neil Dalchau
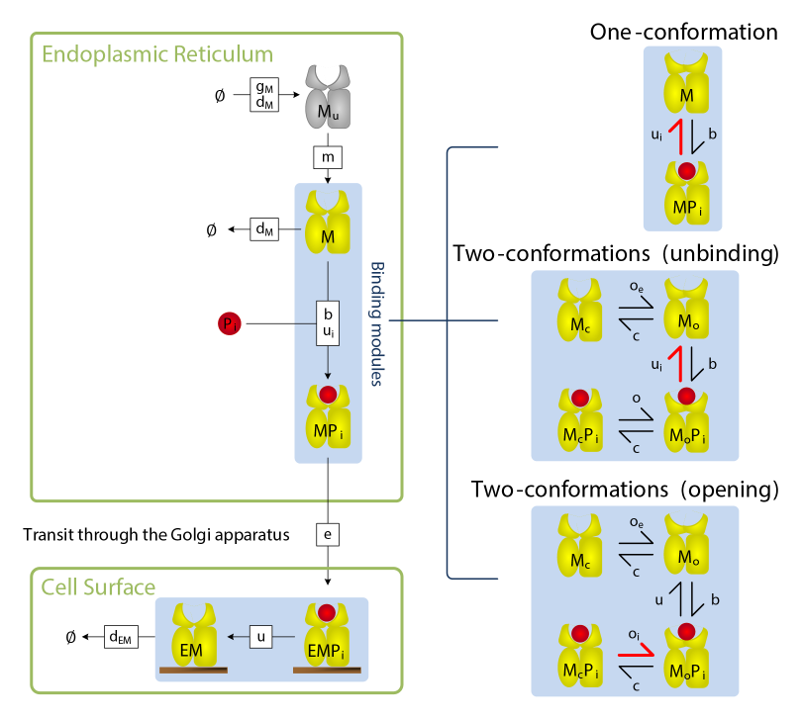
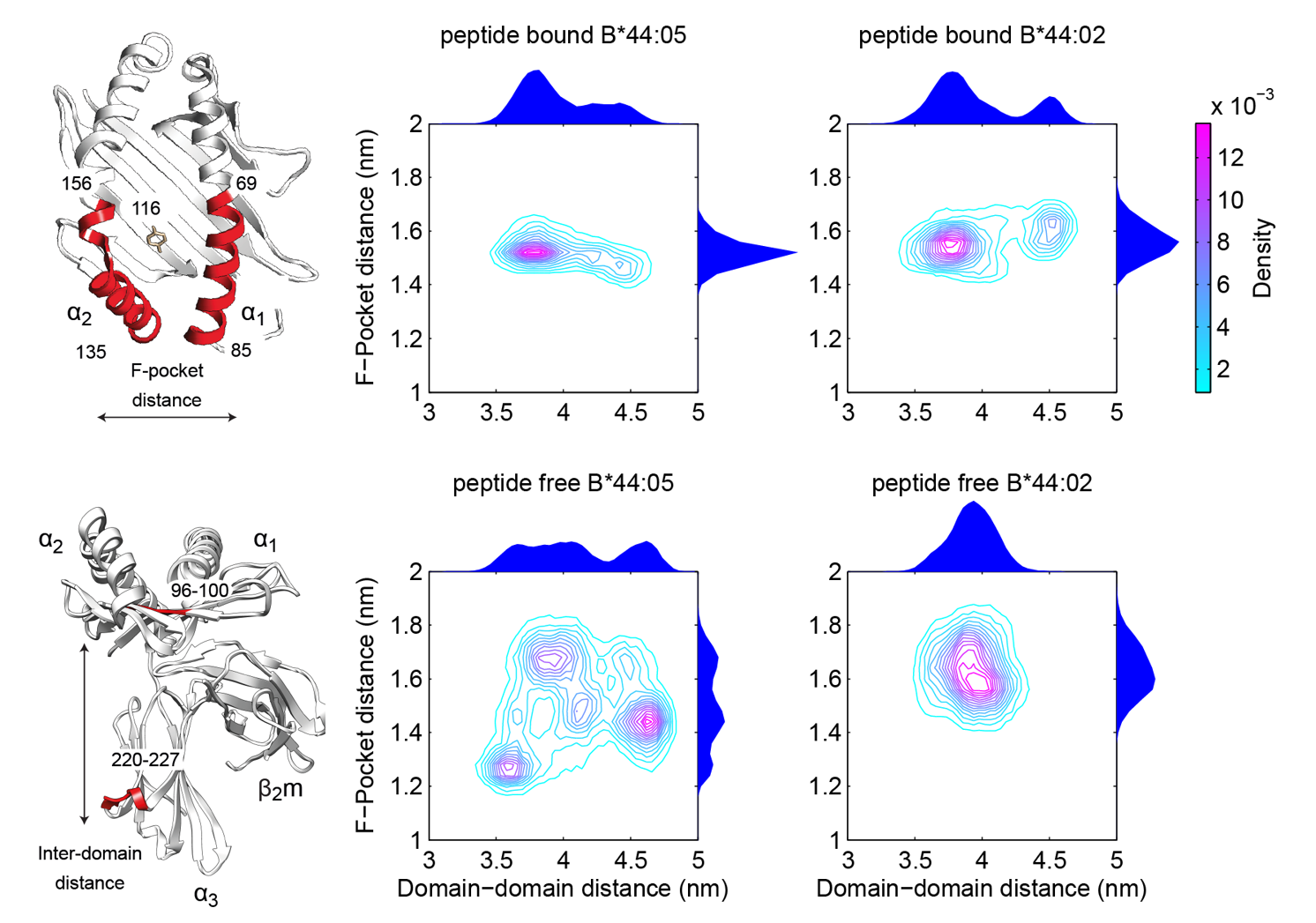
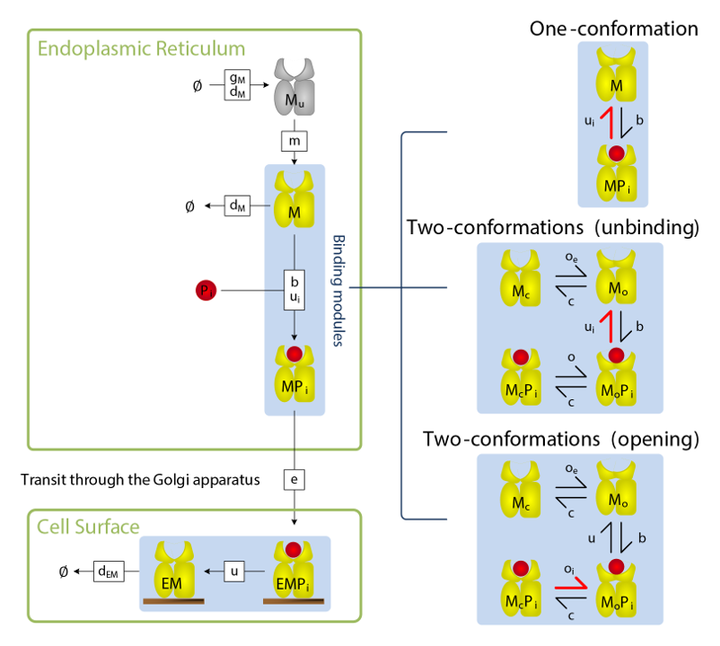
Model of MHC I peptide selection by Neil DalchauThis project sought to explain the mechanism of peptide selection by two functionally distinct MHC I allotypes using a combination of molecular dynamics and mathematical modelling of biochemical experiments.
In collaboration with the Biological Computation Group at Microsoft Research Cambridge we used biochemical data to infer that a conformational intermediate of MHC I is significant for peptide selection, and molecular dynamics simulations to show that peptide selector function correlates with protein plasticity.
This led to the proposal that MHC I cofactor tapasin modulates MHC I plasticity by dynamically coupling the peptide binding region and membrane bound domain.
Publication
A. Bailey, N. Dalchau, R. Carter, S. Emmott, A. Phillips, J. M. Werner, T. Elliott. Selector function of MHC I molecules is determined by protein plasticity. Sci Rep, (5), pp. 14928, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14928, 2015.